Stocks trading
The place to LEARN all about investing in stocks
Stocks overview
Courtesy of TradingView

All about stock trading
Most beginner investors, initially look into stock trading. Early investments were associated with the stock market and predate a lot of the other asset classes available for trading today.
History of stock trading takes us back to the 1400s, where opportunities and stock in the “new world” was sought after. Trading of spices, textile and commodities was prevalent, and money was needed to fund expeditions. There you have your first investors, that would fund these trips in return for a share of the profit i.e. dividends.
From the establishment of the first stock exchange in Amsterdam in the early 1600s and all the way to present day, major developments in technology, regulations, globalization enabled investors of any size, to engage in stock trading activity.
How do stocks
become available to trade
Must be agreed by the board of directors, and the number of new issues is defined at incorporation
First offered to current shareholders, new issues are typically common stock to increase capital
Companies are looking to raise capital for expansion, R&D, pay off debts, public perception and other reasons

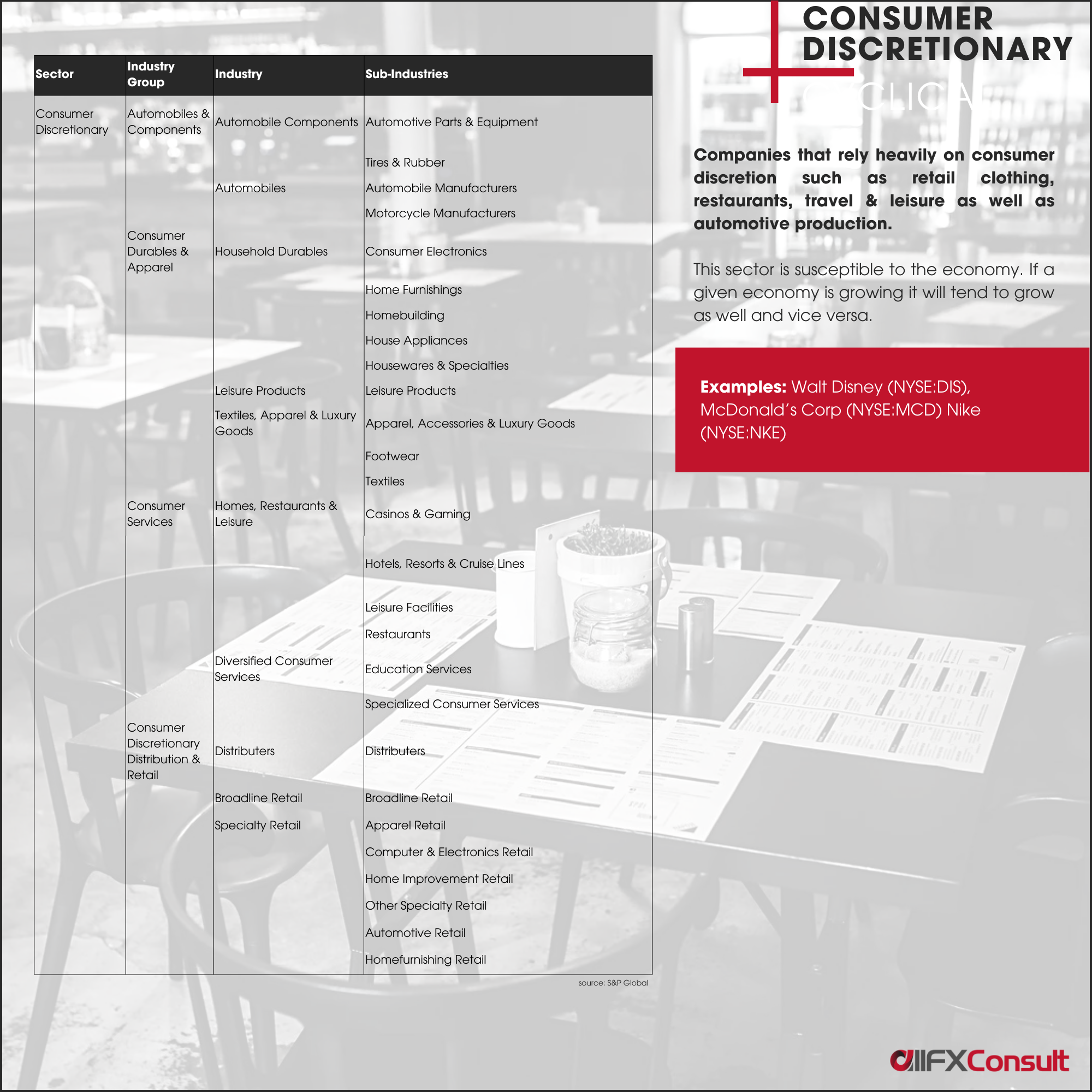
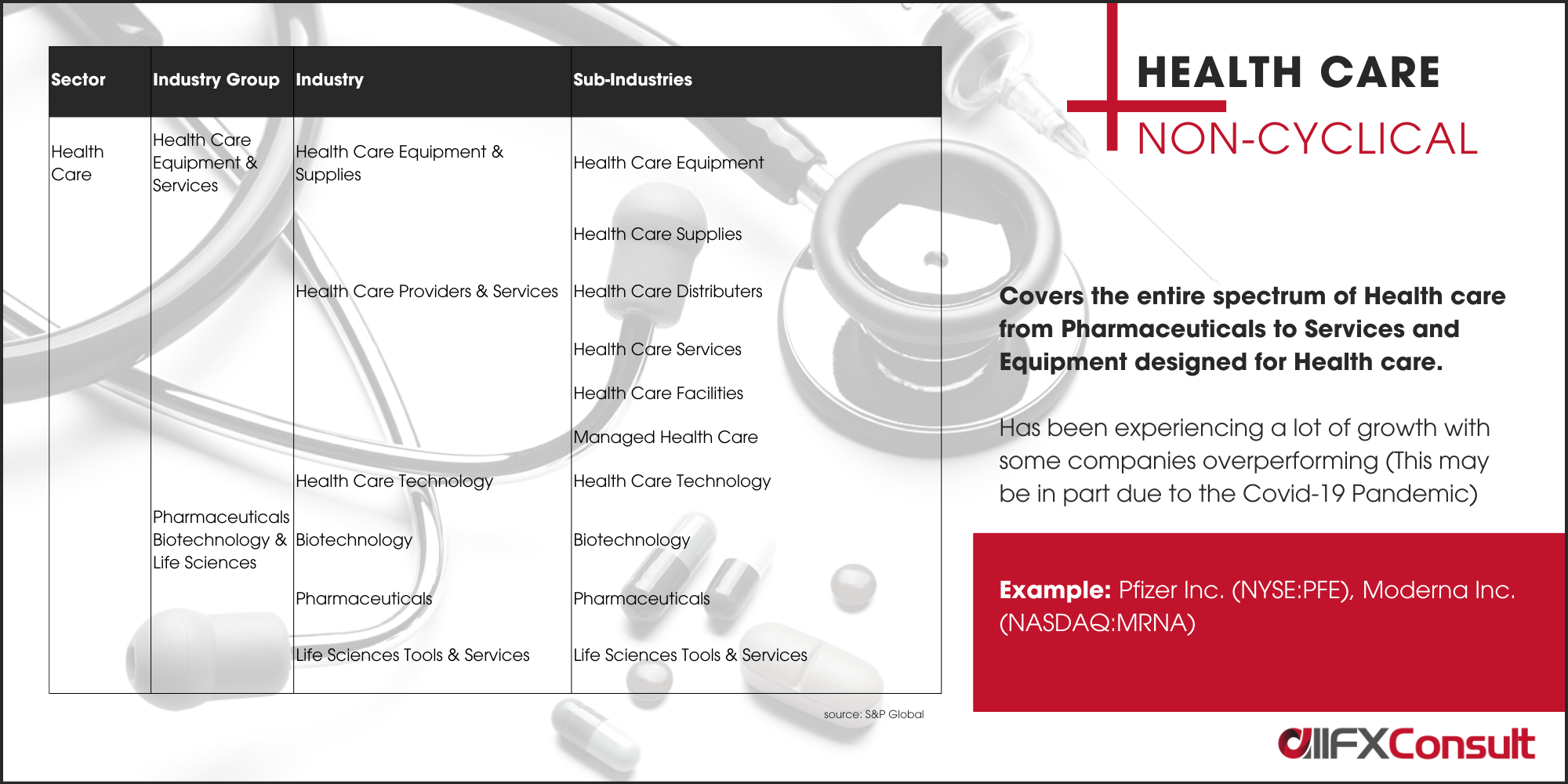
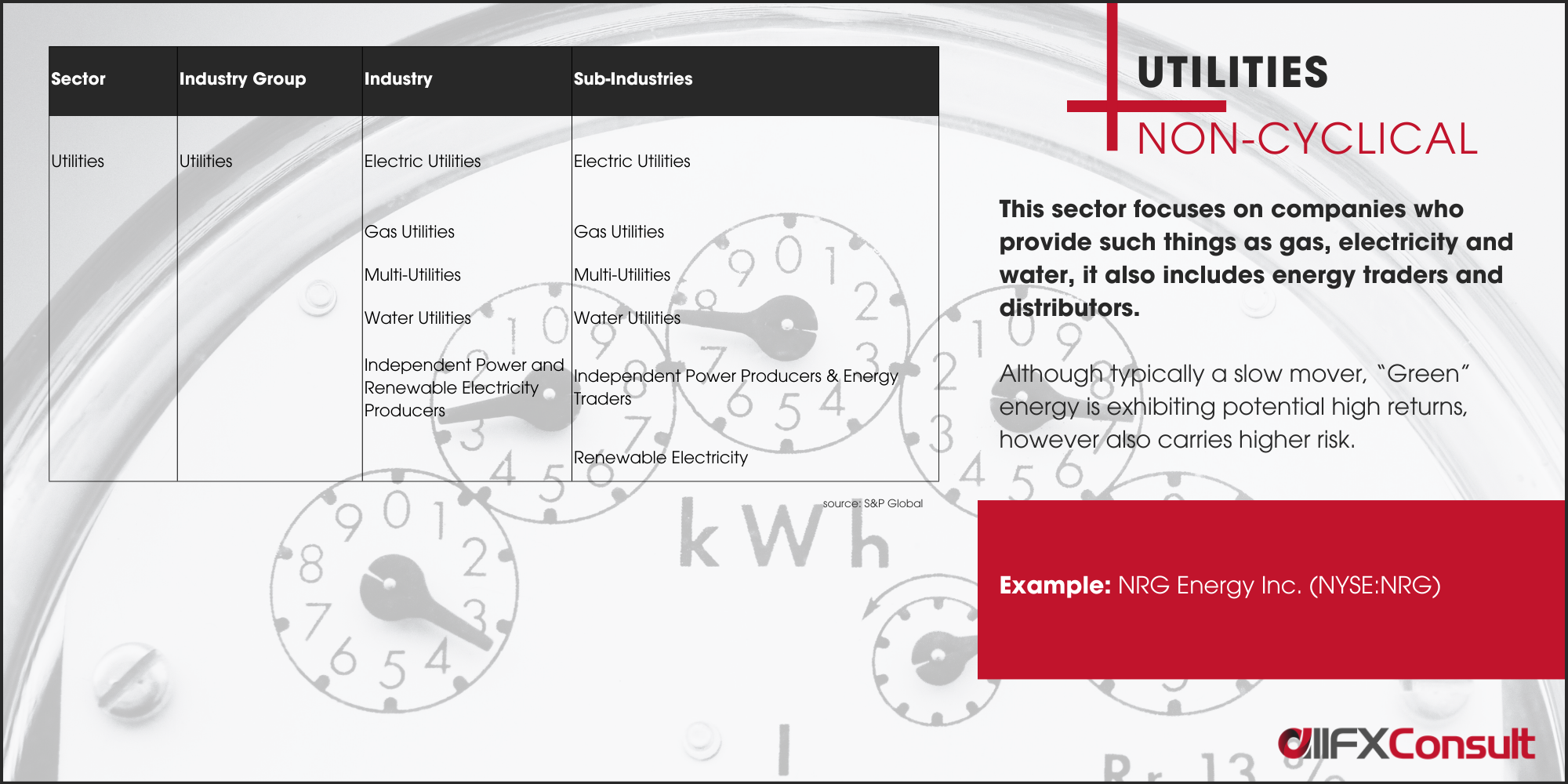
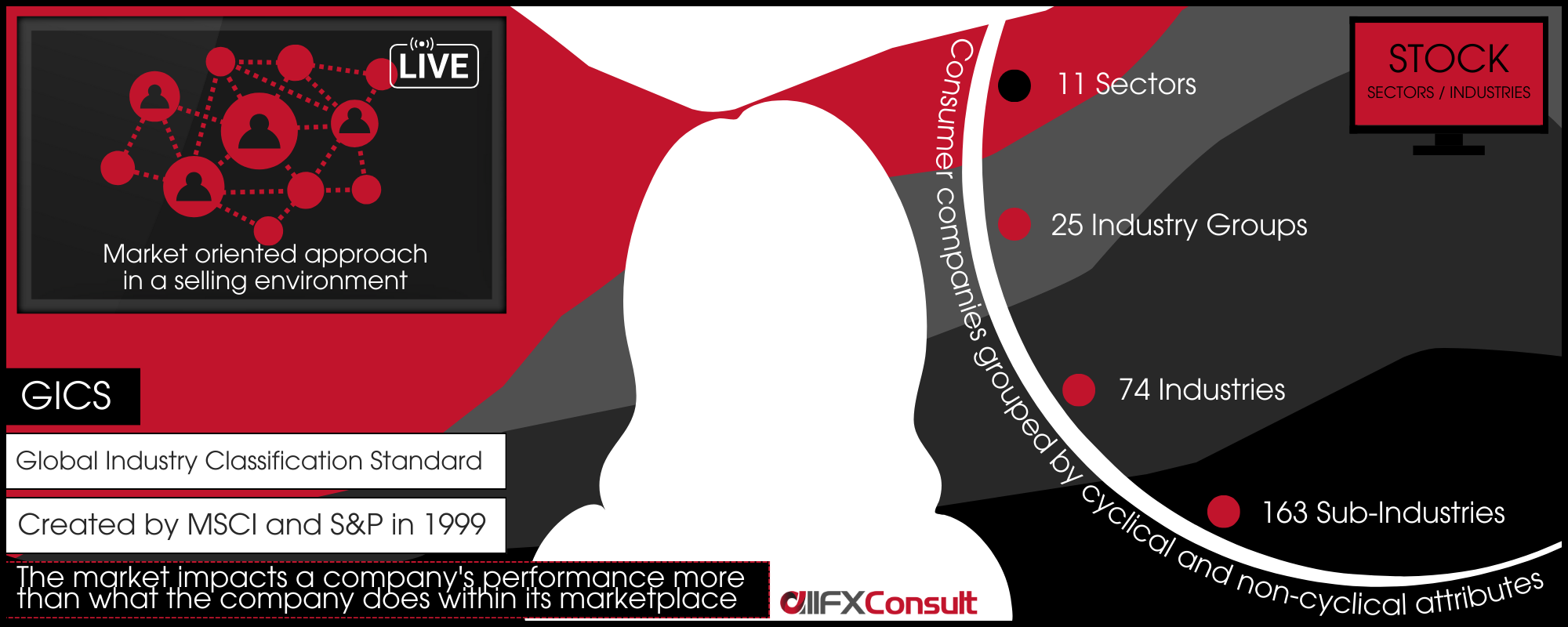
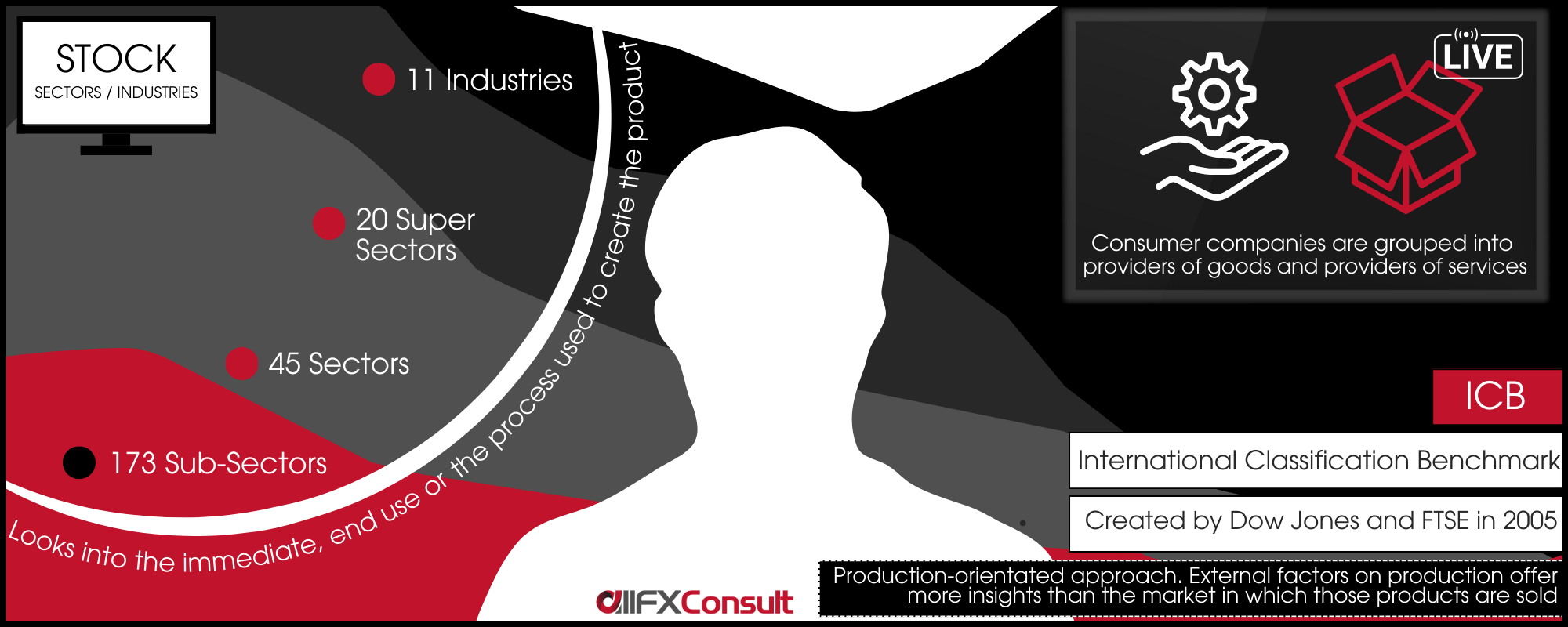
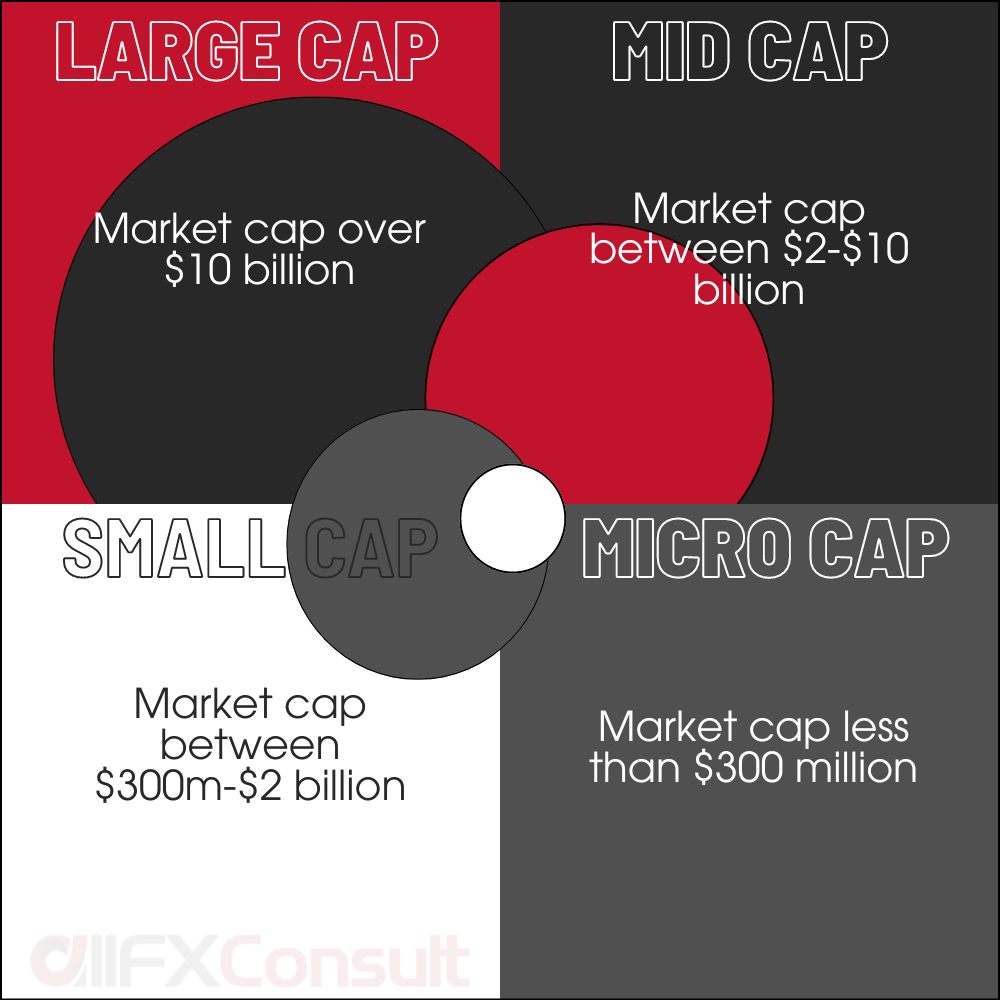
Types of stocks
Other than the sector classification, stocks can be grouped by type

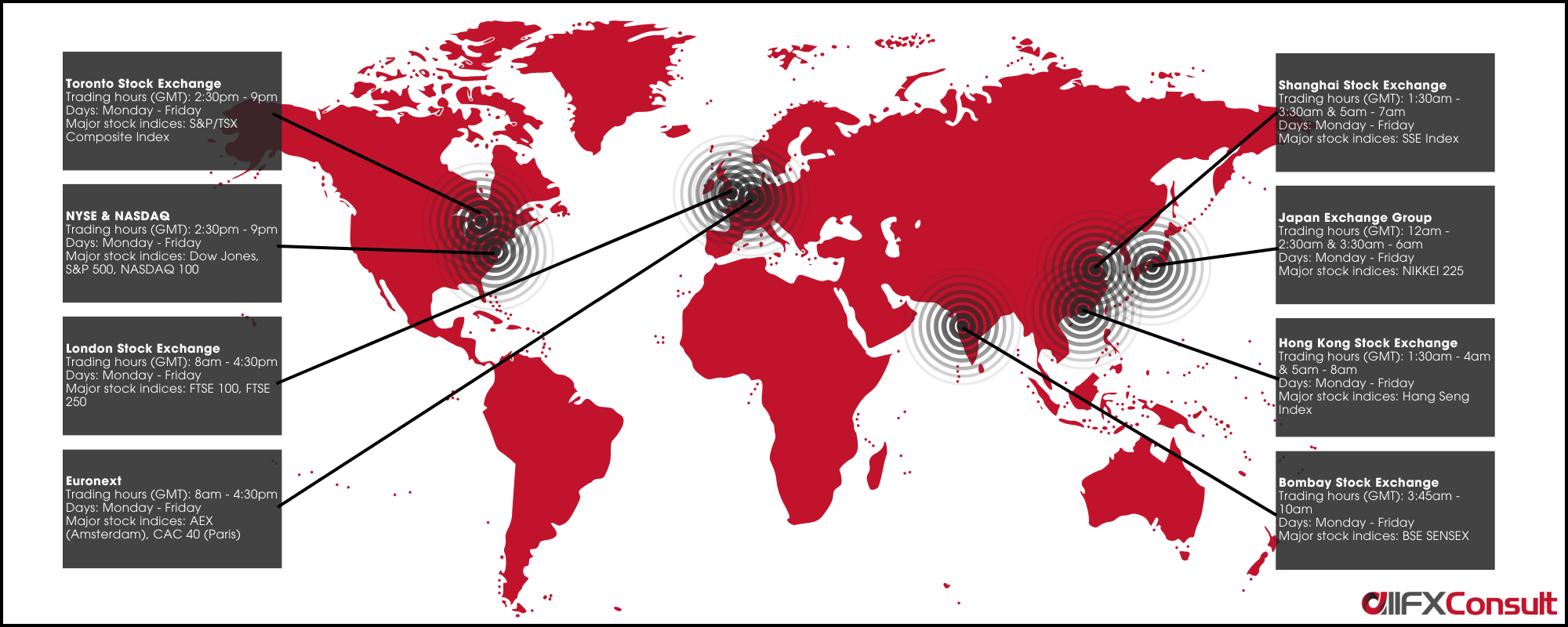
Stock exchanges
what and when?
Stock exchanges are organized marketplaces, that provide the infrastructure for investors to trade (buy and sell) shares/stocks of publicly listed companies. They are heavily regulated with many requirements prior to listing a company and provide a safe intermediate between buyers and sellers of listed shares.
There are over 80 stock exchanges operating globally with a combined market cap of over $110 trillion. We included the trading hours of some stock exchanges in the image below.
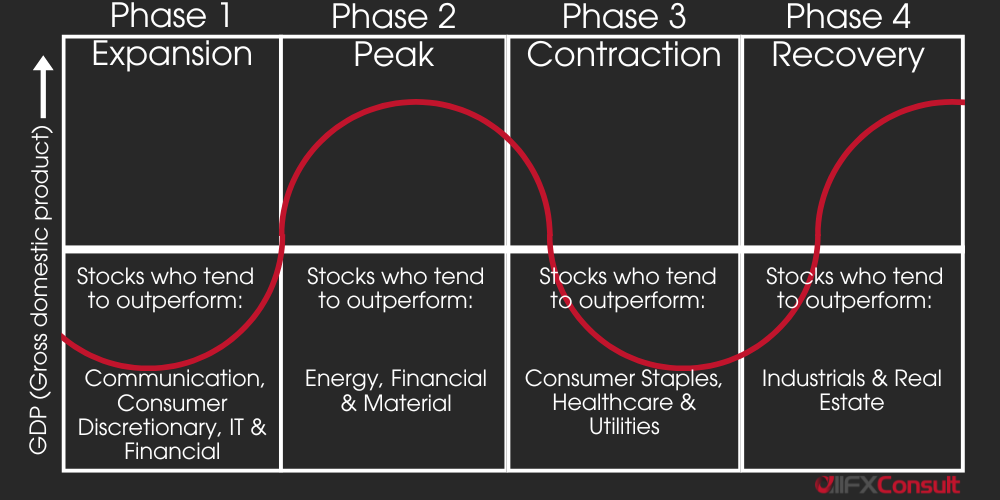
Factors that affect stock prices
National policies, global relationships
Volume, liquidity, sentiment, buy/sell pressures
Economy and fundamental indicators
Natural disasters, disease, pandemics
Company fundamentals, earnings reports
Especially multinational companies
Special attention to earnings reports
How to trade stocks?
What is a stock, trading structure, trading hours, CFDs
Earnings, multiples, screeners, spread, price movers
Customize market and stock screeners for stocks
Margin, margin call, stop out, leverage, contracts
Stop loss, trailing stop, take profit, pending orders
Fundamental, technical, sentimental analysis
Trader types, risk tolerance, start small, pick direction, test
Strict selection process, open a/c, KYC, funding, trade
Trading log, review, evolve, socialize, use technology
Profitability, how to choose a broker, what to trade?
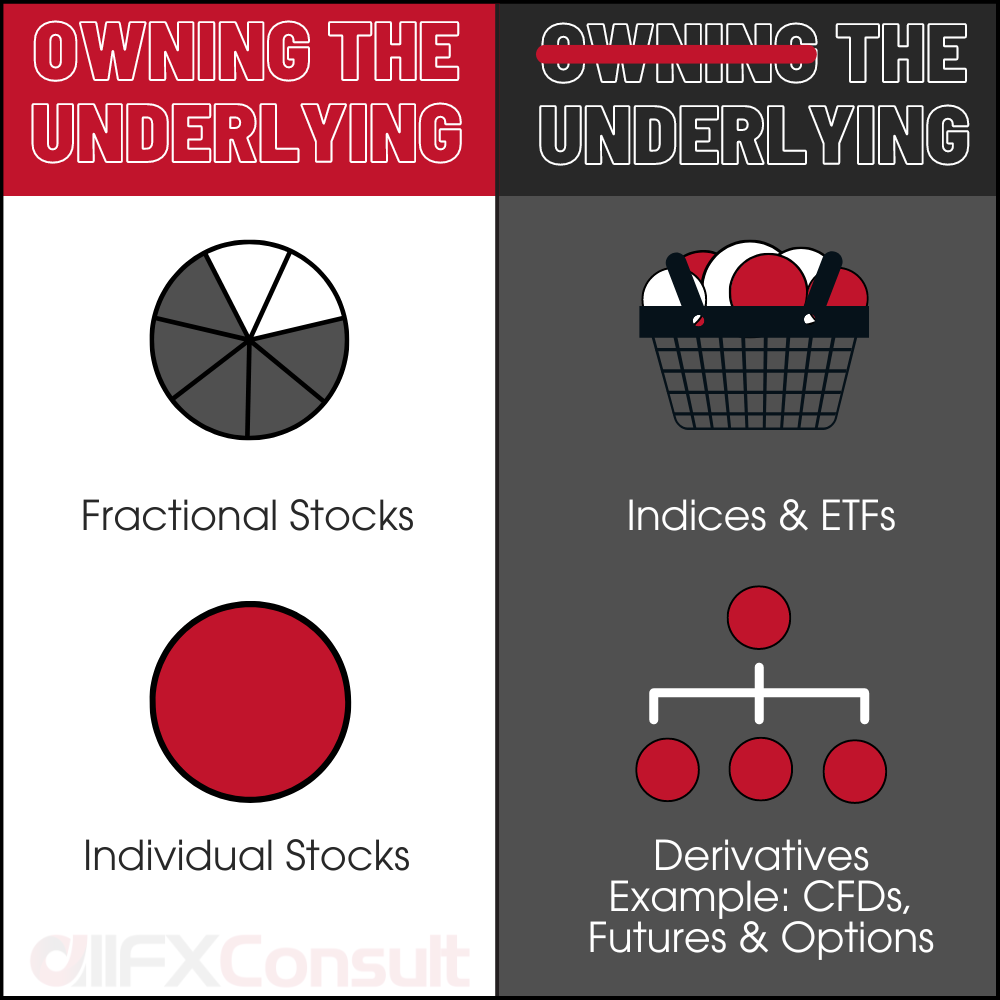
Stocks can be traded by owning the underlying stock, either in full or partly (fractional). This type of trading is targeted towards retail investors that have a medium to long (buy and hold) strategy in mind although short term traders use this as well.
Stocks can be traded through derivatives. These products don’t involve ownership of the underlying stock and are targeted towards traders aiming to ride the price fluctuations for a quick return. Examples include CFDs, futures and options.
Traders and investors can also gain exposure to stocks through basket products like indices, funds and ETFs. These products help with diversification, passive investing and can target a larger segment of a sector, market or economy.
Learn to diversify
Pros of stock trading
Cons of stock trading
Relatively high returns – with correct analysis, stocks can yield higher returns than other assets
More than one income stream – possible returns through capital gains and/or dividend payouts
Liquidity – many stocks attract high interest – there’s almost always a buyer to a seller and vice versa
Regulation – stocks trade on exchanges, that minimize cases of fraud or market manipulation
Array of options – with thousands of stocks available, traders have many options to consider
Volatility – stock trading has multiple influencing factors, making it unpredictable and volatile
Requires time – screening of company financials, market trends, news can be time consuming
Trading sessions – stock exchanges open and close daily, unlike forex which is 24 hours 5 days a week
Centralized – unlike forex, stock trading is centralized, with loopholes that may allow potential manipulation
Impulsive trading – multiple sources of online misinformation, may enable impulsive trading decisions
FAQs
Where do I begin in order to invest in the stock market?
Consider answering questions like what type of trader am I, how much money can I allocate to stock trading, what is my risk tolerance, am I looking for short or long trades, how will I manage my risk, how will I diversify? Our website is a good place to start answering some or all of these questions.
Can anyone trade stocks?
Any individual of legal age, who has funds that can be allocated to stock trading without affecting other finances, and possesses the necessary knowledge can trade stocks.
What are the best stocks to trade?
There are thousands of stocks available to trade. All of them require time, analysis and research to make the appropriate decision in connection with the trader’s investment goals.
How can I practice trading stocks?
All brokers offer virtual accounts known as demo accounts, that allow a trader to experience the broker’s trading environment. I tandem with demo accounts, there are live accounts that allow very small transactions, to become accustomed to the psychology of real trading.
What are fractional stocks?
To understand fractional stocks, you can think of a stock like a pie. By cutting the pie in multiple pieces, you create fractions of the pie. Fractional stocks aim to split the stock in manageable parts, that can cater to smaller investors.
Thinking of monetizing your network?
For any questions or concerns
Our team is available 24/7